When it comes to post-training nutrition and fasting, men and women are not the same. While much of the mainstream advice on nutrition and recovery is based on research conducted on men, emerging studies—led by experts like Dr. Stacy Sims—highlight the critical differences in how women should approach fueling and recovery. From the shorter post-training refueling window to the negative effects of fasted training, women need a tailored approach to optimize performance and long-term health.
Post-Training Nutrition: Why Women Need to Refuel Sooner
After training, the body enters a recovery phase where it repairs muscle tissue, replenishes glycogen stores, and shifts from a catabolic (breakdown) state to an anabolic (building) state. The timing of this recovery process differs significantly between men and women.
Men have a longer window to refuel. Research suggests that men can maintain an elevated metabolic rate and glycogen resynthesis for up to three hours post-training. This gives them more flexibility in delaying post-workout meals.
Women need to refuel within 30 to 90 minutes. Women’s metabolisms return to baseline much faster—typically within 60 to 90 minutes—meaning that delaying nutrition can hinder muscle repair and recovery.
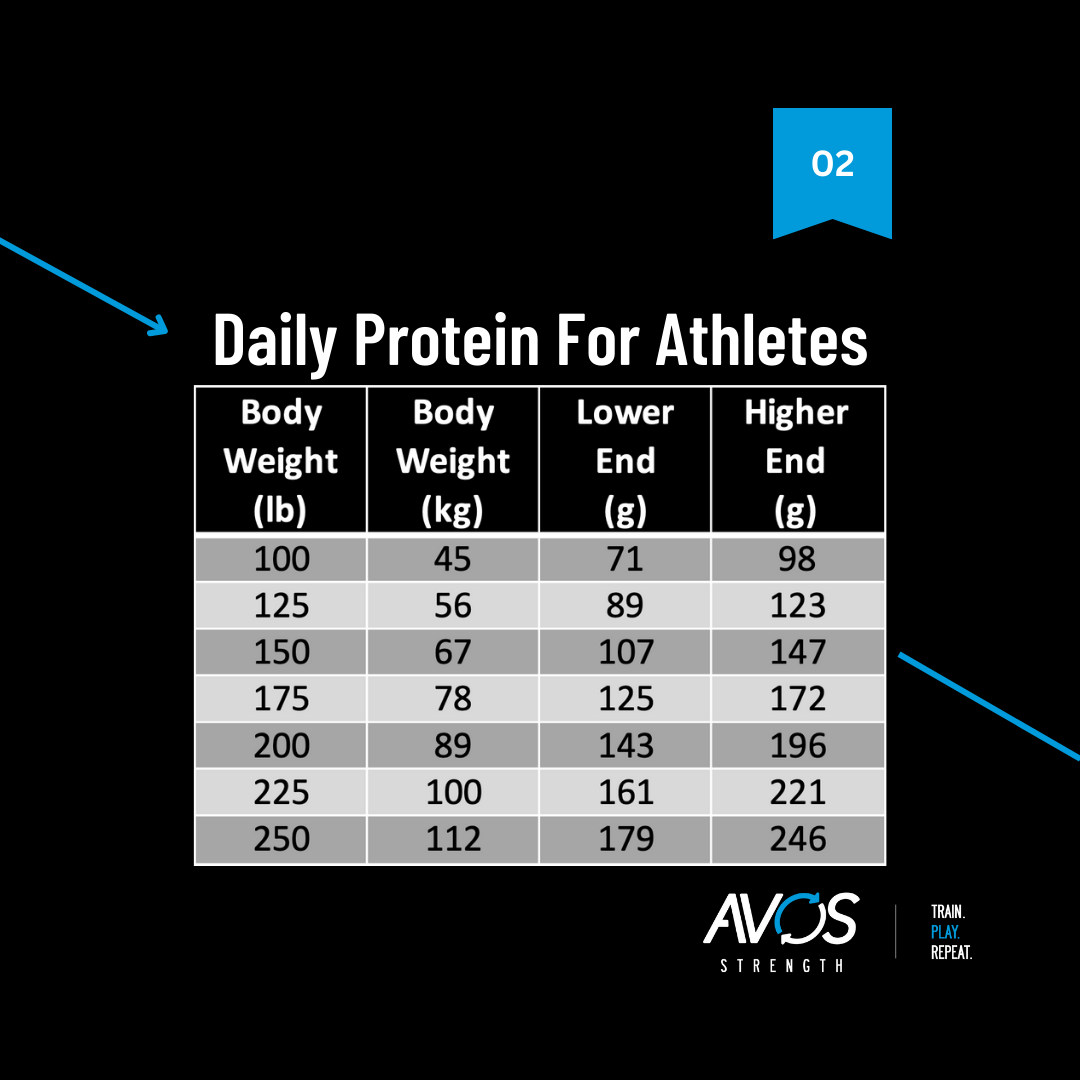
Dr. Sims recommends that women prioritize at least 35 grams of high-quality protein within 45 minutes of finishing a training session. Pairing protein with carbohydrates helps replenish glycogen stores and prevent excessive muscle breakdown.
The Problem with Fasted Training for Women
Fasted training—exercising on an empty stomach—is often promoted as a tool for fat loss and metabolic efficiency. While this approach may work for some men, the physiological response in women is quite different, often leading to more harm than good.
1. Hormonal Disruptions
Women’s bodies are highly sensitive to energy availability. Training in a fasted state can disrupt key hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and cortisol, leading to negative effects such as irregular menstrual cycles, decreased thyroid function, and metabolic slowdowns.
2. Increased Stress Response
Morning cortisol levels are naturally high, and exercising without food further elevates stress hormones. This can lead to:
Increased muscle breakdown
Higher levels of fatigue
Poor recovery over time
3. Impaired Performance and Recovery
Without adequate fuel, women often struggle to reach high training intensities. This means workouts may be less effective, leading to slower progress in strength and endurance. Additionally, prolonged fasted training can contribute to low energy availability (LEA), which has been linked to increased injury risk, poor immune function, and chronic fatigue.
What Women Should Do Instead
Instead of training fasted, Dr. Sims suggests women eat a small pre-training snack containing protein and carbohydrates, such as:
A banana with a small amount of nut butter
Greek yogurt with berries
A protein shake with half a scoop of whey and some oats
Then, follow up with a proper post-training meal that includes a balance of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to optimize recovery.
Final Thoughts
The takeaway? Women need to refuel sooner post-training and avoid fasted exercise to support optimal hormone function, performance, and long-term health. While men may have a more extended recovery window and can tolerate fasting with fewer consequences, women benefit from a more consistent intake of nutrients throughout the day.
By adjusting nutrition strategies to align with female physiology, women can maximize their training results, recover more efficiently, and sustain long-term health and performance.
For more insights, check out Dr. Stacy Sims' work, including her books and podcasts on women’s health and performance.